
This way, this uva uvb grow lights duplicate the natural sunlight in a very close range. Most of the grow light available contains the entire visible spectrum and a few ultraviolet lights. But when you expose them to a few UV lights when they are indoors germinating in their early stage, shock from outdoor transplanting can be reduced drastically. This is because the light intensity outdoor may be too high for them to adjust. If you transplant them from indoors to outdoor, they might go into shock.
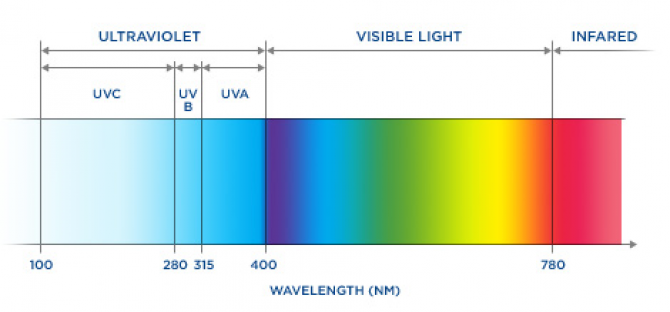
Reduces Plant Shock: When your plants are still indoors germinating, they are still fragile to high light intensity. Enhance Germination: The germination process of indoor seeds that are just starting can be promoted by ultraviolet lights. VIVOSUN 48″x24″圆0″ Grow Tent with Observation Window and Floor Tray Fortunately, UVC light rays are filtered out entirely from the Earth’s surroundings. It is even used for sterilization uses to kill harmful microorganisms. The UVC light is extremely energetic and it’s capable of killing living cells. UVC: the wavelength of ultraviolet C ranges from 100 to 290nm. The good news is that nearly all of the sun’s UVB rays are obstructed by the Earth’s ozone layer. The UVB light rays are capable of causing damage to the DNA of cells and they can as well cause cancer in living cells. It makes up about 0.15% of natural the entire sunlight. UVB: the wavelength of the ultraviolet B ranges from 290 to 320nm. You should however know that UVA lights for plants do not cause DNA impairment. UVA light makes up most of the entire amount of UV light on the earth. The natural light that passes through the earth is made up of 3% UVA light. UVA: the ultraviolet A wavelength ranges from 320 to 400nm. There are 3 different types of ultraviolet lights and they include: Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation which has radiation shorter than visible light and is present in the sun. UVB light is produced by plants in sunlight.Ĭonclusion On UVA/UVB Lights For Plants Ultra Violet Lights & Their Types UVB is known as the “sunlight” of the plant world, and it’s essential for flowering. It is one of the most common questions we get asked by people who are new to growing cannabis indoors. There is a myth in the cannabis community that LED grow lights do not produce ultraviolet B (UVB) light. Without this, the plant would be suffocating. It causes plants to open their stomata, or pores, which allows air and carbon dioxide in and water out. UV-B is the most harmful of these wavelengths, and can cause a sunburn on your plants, but UV-A is actually beneficial to plants. Yes, grow lights have both ultraviolet (UV) A and ultraviolet (UV) B wavelengths. It can’t flower or fruit if it doesn’t get enough UVA and UVB. The blueberry needs a lot of UVA and UVB to flower and fruit. The only plants that I know that require both UVA and UVB are the blueberry. As a result, the UVB radiation we receive at ground level is relatively small. The UVB part of the spectrum is filtered out of sunlight by the atmosphere. This penetration is dependent upon the amount of ozone in the stratosphere. The UVB radiation (wavelengths 320 nm to 280 nm) penetrates the atmosphere and does not penetrate the stratosphere. 
This penetration is dependent upon the amount of ozone and the wavelength of the UVA light. UVA radiation (wavelengths 400 nm to 320 nm) penetrates the atmosphere and can reach the surface of the earth.
Uva uvb uvc wavelength skin#
This causes damage to plant cells and can result in sunburns, which can be painful and cause skin damage if the exposure is too long.

UVB is important to plants because it causes plant tissue to darken. Plants cannot use this portion of the spectrum for photosynthesis or other biological functions.
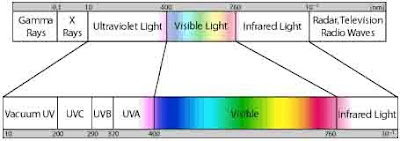
UVB is the part of the spectrum that is filtered out by the atmosphere and clouds. UVA is used by plants for photosynthesis and other cellular functions. It is a component of sunlight and is not filtered by clouds or the atmosphere. UVA is a part of the visible light spectrum that we see as white or yellowish light. Plants use both of these parts of the spectrum for different purposes. The ultraviolet (UV) spectrum is divided into two parts: ultraviolet-A (UVA) and ultraviolet-B (UVB).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
